What is a Switch in Networking? Comprehensive Guide to Network Switches
Table of content
Introduction:
You must have some basic knowledge of a network switch if you have landed here. However, there has always been a plethora of fresh updates on all networking devices as the fields itself is ever-growing. A network switch is a hardware device used in computer networking that enables communication between devices, such as computers, wireless access points, printers, and servers, connected to a local area network (LAN). At its core, it works as a central hub that facilitates multiple devices to connect and communicate with one another to share resources and information. Unlike a hub, which broadcasts data to all connected devices, a switch intelligently directs data packets only to the device for which it is destined, making it more efficient and secure. In the present network landscape, modern switches are equipped with advanced features such as Quality of Service (QoS) prioritization, VLAN support, and even Power over Ethernet (PoE) capabilities. Here, we have come up with this blog to give some unheard information you would have missed somewhere else. Thus, move ahead step by step know the things you have been searching for so far.
What is a Network Switch:
A network switch is a device that interconnects various devices often on a local area network (LAN). It forwards data back to and from those devices. Many people think of a network switch and router as the same but the reality is something else. A switch sends data only to the particular device it is destined to. A network cannot send data packets to more than devices at the same time. According to Wikipedia, “A network switch (also called switching hub, bridging hub, and, by the IEEE, MAC bridge[1]) is networking hardware that connects devices on a computer network by using packet switching to receive and forward data to the destination device.”
Working of A Network Switch:

Take a look at the following short points to learn about the science behind how a network switch works:
- The network interface card (NIC) on the device sends its media access control (MAC) address to the network switch, which stores it.
- The MAC address tells the switch how to send packets to and receive packets from the linked device.
- MAC addresses are unique numbers that don’t change, but IP addresses can.
- Switches read the heads of packets, check to see if they are going to the right place, and send them through the right ports.
- Switches use full-duplex functionality to keep network traffic from colliding, which lets two-way contact happen at the same time.
- Switches work mostly at Layer 2, but they can also work at Layer 3 to handle virtual LANs (VLANs) and route traffic between subnets.
Features Offered By A Network Switch:
Speed of the port:
Port speed is crucial as it shows how fast data can flow through a single port. A device that needs a lot of bandwidth need faster port speeds to ensure that data can flow seamlessly across the network.
Density of ports:
A high-density network switch functions well with networks that have a lot of devices, while a low-density switch works well with networks that have fewer links. Besides, The speed of data processing is also affected by the type of ports ranging from Gigabit Ethernet to 10 Gigabit Ethernet.
Managebility
A network switch, like Cisco network switches, has an easy-to-use interface that makes setting it up and configuring it quick and easy. A network switch also has a lot of useful features, such as Quality of Service (QoS) to help you decide which data is most important.
Scalability:
You can add more ports to a flexible network switch as needed without having to buy a whole new switch. It’s also important to support enough VLANs (Virtual Local Area Networks) to divide the network into sections and make traffic handling better.
Energy Efficiency:
Using network switches that are energy efficient can cut costs by a large amount. Energy-saving modes, such as power-saving mode or port shutdown, and features like Energy Star approval help keep energy use low.
Advanced Security:
For keeping the network safe, security measures are very important. So, a switch lets you protect its ports by limiting the number of MAC addresses that can connect to each one or stopping data from certain MAC addresses.
Budget:
Depending on what features and functions they have prices for network switches change a lot. However, there are cheaper choices for people with limited budgets, while bigger setups may need a bigger investment.
Network Switch That You Need:
You need to decide which network switch is best for your machine. To pick between different network switches, you just need to follow a few easy steps. You can count on us to help you, though. You know there are different kinds of switches, mostly controlled and unmanaged ones. There are many thoughts going through your mind about which one to pick. Once you understand how the different switches work, the process is pretty easy. So, let’s talk about the most popular switches: managed switches and unmanaged switches.
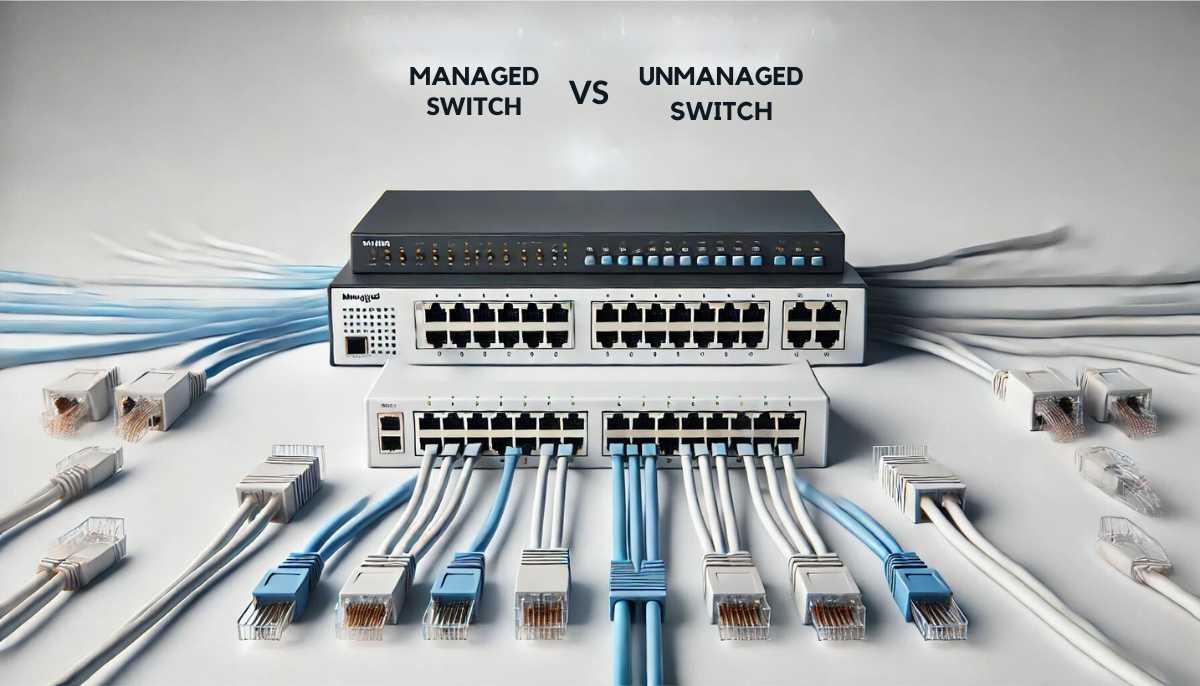
Managed vs Unmanaged Network Switch:

One thing is common in almost every business setup; to consider your needs and requirements and deploy appropriate equipment. The same case is applied when you choose between managed vs unmanaged switch. But, before you select one of them, it is crucial to see what sets them apart.
To cut the story short, an unmanaged switch is a plug-and-play type of network device that starts functioning without any configuration and is more suitable for small businesses to tackle some fundamental needs.
On the other hand, a managed switch offers more data on performance and is customizable with further configuration options. Its robust features and diverse options make it a go-now choice for large enterprises and complex networking systems.
Managed vs Unmanaged Switch In A Table:
| Feature | Managed Switches | Unmanaged Switches |
|
Capabilities |
Offers configurable features for diverse deployment, optimizing network performance and availability. | Limited to basic functions like negotiating transfer speeds and duplexing. No advanced features or configurations. |
|
Security |
Provides configurable security settings to protect the network and identify threats. | Lacks security capabilities. Does not offer protection or threat detection. |
|
Cost |
More expensive due to advanced capabilities; additional cost for staff needed to manage and maintain the network. | Cheaper and simpler to operate. Offer minimal initial and ongoing costs. |
Switch vs Router: Differences and Similarities:
A witch connects multiple devices in a building or on a campus and lets them share information and resources.
A Router connects different switches and their respective networks to establish a larger network.
You may find similarities between a router and a switch but the main difference lies in their working principles and the nature of ways they choose to perform their actions.
MAC Address and IP Address:
MAC (Media Access Control) addresses are unique identifiers assigned to network interfaces for communications on the physical network segment. Essential key points:
- Hexadecimal address comprising six bytes.
- Oriented toward hardware; linked to the device’s network interface card (NIC).
- Supplied by the manufacturer of the NIC card.
- Immutable over time, retaining the same value regardless of network environment.
- Uses ARP (Address Resolution Protocol) for retrieving device information.
- Functions at the data link layer of network models.
- Specifically structured as six groups of two hexadecimal numerals separated by colons or hyphens (e.g., 00:FF:FF:AB:BB:AA).
- Not divided into classes.
- More secure against unauthorized discovery compared to IP addresses.
- Essential for communication data forwarding in network switches.
IP (Internet Protocol) addresses are used to identify devices across a network or the internet at the network layer. Essential key points:
- Consists of either 16 bytes (IPv6) or 4 bytes (IPv4).
- Oriented toward software; represents the logical location of a computer on a network.
- Provided by an Internet service provider.
- Can change based on time and network environment.
- Uses RARP (Reverse Address Resolution Protocol) for information retrieval.
- Operates as a network layer protocol.
- IPv4 uses dotted decimal notation (e.g., 192.168.1.1), while IPv6 uses hexadecimal notation (e.g., FFFF:F200:3204:0B00).
- IPv4 addresses are classified into A, B, C, D, and E categories.
- Vulnerable to discovery by third parties.
- Necessary for communication data forwarding in routers and supports both multicasting and broadcasting.
A network switch functions at Layer 2 (Data Link layer) of the OSI model and uses a MAC address to forward data packets within a local area network. Switches typically maintain a MAC address table that helps network switches recognize which devices are connected to which ports.
A router operates at Layer 3 (Network layer) and uses an IP address to route data packets between different networks. It maintains a routing table that paves the way to various network destinations based on IP addresses.
The Best-ever Network Switches in 2024:
Looking for the best network switches for your network infrastructure? If yes, then the answer is ‘Cisco Switches’ that offer performance, flexibility, and security. In addition, these network switches are scalable and cost-efficient and meet the demands of hybrid work.
Learn more about Router Switch
Conclusion:
Although network devices are in immense use today. But, only a few people are successful in choosing the right for them because the are always misguided, unfortunately. We hope to have provided you with an expert, research-driven, and authentic guideline on network switches you can use to revolutionize your current network infrastructure. We encourage you to keep visiting us for further updates.
Frequently Asked Questions:
What are the common types of network switches?
Some common types of network switches include managed switches, unmanaged switches, PoE switches, and stackable switches. All these switches have particular features and use cases.
What is a Cisco switch?
Cisco switches are networking devices that connect multiple devices, such as computers, wireless access points, printers, and servers on the same network within a building or campus. These switches enable connected devices to share information and talk to each other and offer unparalleled features as compared to others in the industry.
What are the benefits of deploying a network switch?
A network switch allows network administrators to scale their network infrastructure according to their requirements and needs. Every switch comes with its own specialties offering a plethora of advantages to businesses of all sizes.
How Cisco network switches are beneficial?
Offering improved performance of your network, increased security, better reliability, and ease of use and management, Cisco switches are beneficial for a business and advanced network infrastructure for multiple reasons.




 Catalog
Catalog





















































































































 (800) 870-9487
(800) 870-9487