TCP vs UDP: Which One Is Better?
Table of content
Introduction:
Internet traffic in servers and other devices is divided into data transfers. This data is sent, arranged, and received via two different protocols: TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) and UDP (User Datagram Protocol). Both these protocols do the same job but with varying behavior. For instance, they differ in reliability, speed, and data arrangement. So, how do you know which one is better from TCP vs UDP? This blog has the answer. We will explore the differences between TCP and UDP, as well as their benefits, drawbacks, and more. Keep reading this blog and learn everything you should know about TCP and UDP.
TCP vs UDP: What Is The Difference?
The main difference lies in their reliability and status of connection. TCP is a connection-based protocol and is more reliable while UDP is connectionless is not as reliable. Besides, TCP data transfer rates are slower than UDP. While both these protocols govern the methods through which data is transferred and received, they differ in various ways providing having features and drawbacks.
What Is TCP (Transmission Control Protocol)?
TCP is the most reliable protocol today. It is a connection-based protocol which means it enables a reliable connection between sending and receiving devices. It transfers data from user devices to the web server. If functions while you send emails, and messages, watch online movies, make calls on skypes, and more. Because of its end-to-end connectivity, it ensures that data reaches its destination timely and perfect.
Function of Transmission Control Protocol:
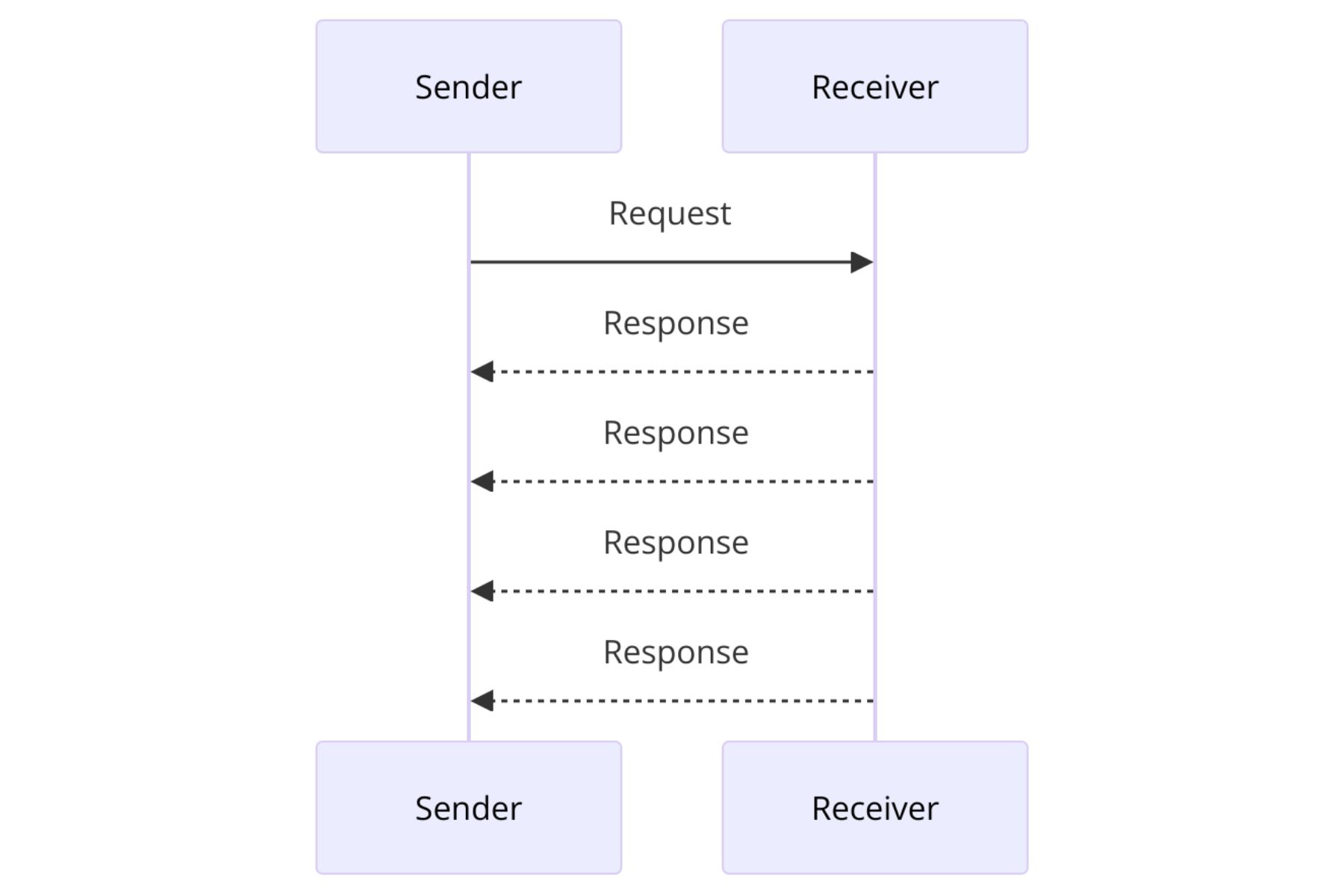
What is UDP (User Datagram Protocol)?
In contrast to TCP, it faster and straightforward but less reliable. Mostly, it is used in scenarios like high-resolution streaming and gaming where higher speeds are required. UDP is connection meaning it doesn’t establish a direct connection between sending and receiving devices. No doubt, it has higher speeds but there are chances of losing data in between.
Function of User Datagram Protocol:
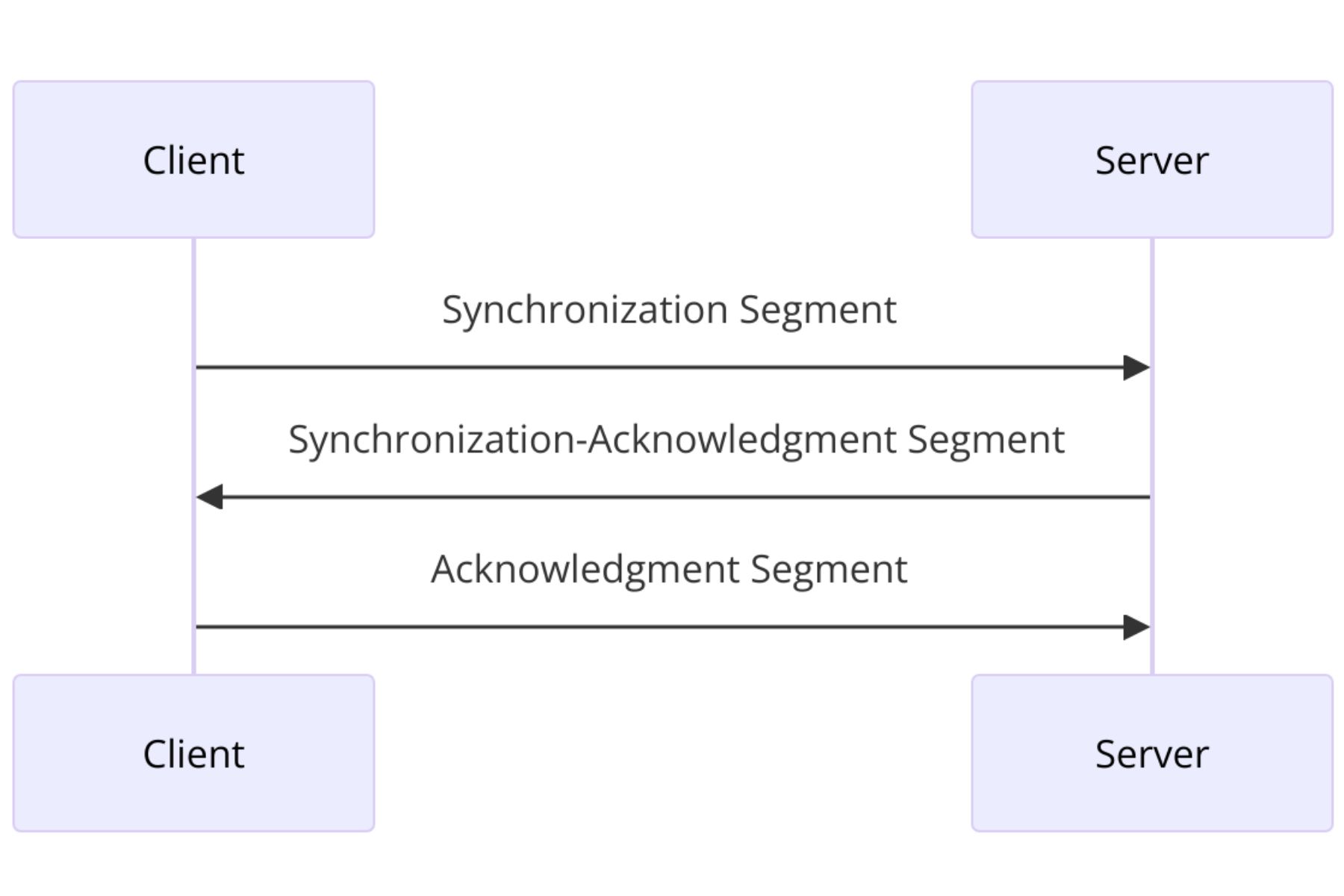
TCP vs UDP Protocol: How Do They Work
Here Is How TCP Works:
- A sequence number (SYN) is sent to the server by the client device that started the data transfer. It instructs the server on what number to start the data packet transfer with.
- The server transmits its own SYN number after acknowledging the client’s SYN. This process is commonly known as SYN-ACK, or SYN acknowledgement.
- The data transfer then starts when the client responds to the server’s SYN-ACK with an acknowledgment (ACK), establishing a direct connection.
Here is How UDP Works:
- UDP sends data to the receiver immediately without confirming delivery or ensuring packet order.
- Known as a “fire-and-forget” protocol, UDP doesn’t establish a connection before transmitting data.
- Unlike TCP, which uses a handshake process, UDP relies on the recipient to interpret the received data.
TCP vs UDP: Advantages and Drawbacks
As mentioned earlier, both these protocols offer a number of advantages while bringing some notable drawbacks. So, let’s have a closer look at their pros and cons to decide which one you should give priority to.
Advantages of TCP And UDP:
| Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) | User Datagram Protocol (UDP) |
| Enhanced interoperability as it operation independently. | Smaller packets higher speeds, less overhead, and lesser delay. |
| Ensures authentic data transmission by error detection and checks. | Data can be lost but it doesn’t affect overall data transmission. |
| Optimizes and alters speed depending on the receiver’s capacity. | Sends data to multiple users at the same time via multicast functionality. |
| Confirms data reaches its destination without being lost. | Faster and more efficient comparatively. |
Drawbacks of TCP And UDP:
| Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) | User Datagram Protocol (UDP) |
| Lot of bandwidth and slower in speed. | Doesn’t confirm exact data transmission. |
| Cannot load the information in case data is lost. | It doesn’t guarantee if the transmission is completed properly. |
| Doesn’t work well in LANs and personal areas networks. | It doesn’t send data in a sequence resulting in unsettled data transmission. |
| It doesn’t support broadcasting functionality | Data delivery isn’t guaranteed, data can be lost. |
Learn more: ONT (Optical Network Terminal): A Detailed Guide
TCP vs UDP: Which One Is Better For You
Keep in mind that both these protocols are useful. It all depends on your needs and which one can work superbly. So, instead of TCP vs UDP ports, think of TCP or UDP in terms of their usage. TCP and UDP function according to the nature of the activity you are doing. For example, if you are watching Netflix or going through a gaming session, UDP is more useful. On the other hand, TCP is crucial when sending files, photos, and emails.
TCP vs UDP: Application and Use Case
Use Cases of TCP:
World Wide Web (WWW): TCP guarantees dependable data transport between your browser and web servers while you view websites.
Email: Sending and receiving emails is done over TCP. Email distribution between servers is handled by protocols such as SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol).
File send Protocol (FTP): To safely send huge files, FTP depends on TCP. TCP guarantees data integrity whether files are being uploaded or downloaded.
Secure Shell (SSH): TCP is necessary for encrypted communication between the client and server during SSH sessions, which are frequently used for remote administration.
Media streaming: TCP is used by websites like Netflix, YouTube, and Spotify to stream audio and video content. Through the management of data chunks and retransmissions, it guarantees fluid playback.
Use Cases of UDP:
Real-Time Multimedia Streaming: Audio and video content can be streamed via UDP. Smooth playing is guaranteed by its minimal latency, even in the event of sporadic data loss.
Internet gaming: UDP is used by many online games to provide quick player communication.
DNS (Domain Name System) Queries: UDP effectively manages these queries when your device looks up a domain.
Network Monitoring: UDP is a lightweight, quick data exchange protocol that is frequently used by tools that track network performance.
Multicasting: Because UDP allows packet switching, it can be used in situations when data needs to be given to several recipients at once.
Routing Update Protocols: To exchange routing information between routers, several routing protocols, such as RIP (Routing Information Protocol), and UDP are used.
Conclusion:
TCP and UDP are both crucial to making your browsing experience better. However, they both have different characteristics when working in particular environments. Despite having a similarity in their functions, there are multiple differences when it comes to TCP vs UDP. So, we have provided you with an in-depth guide that explores their definition, working, pros and cons, and applications. If you still have further queries and want to learn more about networking, visit buyrouterswitch.
Frequently Asked Questions:
Why do we prefer UDP over TCP?
UDP is suitable in streaming and gaming where higher speeds while TCP is suitable for sharing files. TCP, in contrast to UDP, ensures exact data transfer and doesn’t lose the signals in between. Besides, it guarantees that data reaches the right destination through error checks.
Which is safer TCP vs UDP?
As TCP offers error-checking to guarantee that data packets are delivered in the right order, it is more reliable and safer. Besides, it tracks every data packet, prevents all sorts of malicious activities.
Why is UDP faster than TCP?
From TCP vs UDP, UDP is faster than TCP as it doesn’t demand extra responses from the receiving devices. In addition, TCP transmits only particular sets of data while UDP can transmit any sorts of data packets. Most importantly, if some data is lost while streaming, UDP ensures that there is no overall disruption.
Is UDP connectionless?
Yes, UDP is connectionless as it doesn’t establish any prior connection between the sender and the receiver. There is no way for UDP to ensure that the payload is not tampered with. Consequently, data integrity is the application’s responsibility.




 Catalog
Catalog




















































































































 (800) 870-9487
(800) 870-9487