Table of content
Introduction:
Imagine replacing your device’s IP addresses, whether at the workplace or home, every time you connect your device to the network. It can be okay when your devices are not mobilized momentarily, but in the present networking environments where devices are being moved from here and there on a daily basis, reclaiming your IP address daily is a headache. So, DHCP, Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol jumps in to tackle this particular problem. It makes devices learn the IP address automatically. In addition, here emerges DHCP snooping that works as a firewall between trusted DHCP hosts and untrusted hosts. If you are curious about what makes it happen, this blog is all you should put your focus on. We are going to discuss DHCP snooping, its basic concepts, and its configuration in detail. So, let’s start from here.
What is DHCP Snooping?

DHCP snooping is a network security feature functioning at Layer 2 of the OSI model that blocks false messages coming from untrusted/unauthorized DHCP servers. It works like a firewall between devices and DHCP servers where it allows only trusted and authentic responses from trusted servers performing on the network. It examines DHCP traffic and makes sure to block all malicious data that can be used to disrupt network traffic or cause any other security issues.
Using DHCP snooping on the switch helps you to safeguard your network by controlling and monitoring messages that come from untrusted devices linked with the switch. Moreover, DHCP snooping generates and maintains a database called the DHCP snooping binding database that collects information about untrusted hosts with leased IP addresses.
Need Of DHCP Snooping:
In most advanced network setups, DHCP snooping has become paramount. Aside from protecting the network from unauthorized access and malicious attacks, it makes devices like PCs and other trusted devices to make them learn IP addresses automatically. You have to configure DHCP snooping on the Layer 2 switch to protect the host within an authentic network because the untrusted hosts are linked with the Layer 2 switch.
How Does DHCP Snooping Work?

Working on DHCP snooping is pretty straightforward. Let’s make it simpler for you:
First of all, a network administrator enables the DHCP snooping on a network switch to let it know which ports are trusted and which are untrusted.
The second step is to monitor the traffic passing through the switch. Especially, it monitors the requests and responses coming from untrusted ports.
In the third step, DHCP snooping maintains a database in which a valid IP address lease is linked to the port this address was assigned to. This DHCP snooping database tells which IP addresses are valid and to which device they are assigned.
Finally, if a DHCP server response comes from an untrusted port, DHCP snooping blocks it to ensure that only trusted DHCP servers can assign an IP address. This is how DHCP snooping protects a network.
DHCP Snooping Concepts:

DHCP snooping was introduced by Cisco as a unique security feature in their network switches. All other vendors in the realm of networking have been using such features in their operations since then.
DHCP snooping works on the concept of having one or more trusted ports that are attached to authorized legitimate DHCP servers. The clients communicate on the network, the switch starts to maintain a database that houses the Clients’ MAC address, address assigned by DHCP, switch port, VLAN, and available DHCP lease time. This is where the switch filters the unauthorized messages to safeguard the operating system.
DHCP Snooping Configuration:
Step 01: Kick-start configuring DHCP snooping using the command ip dhcp snooping according to the following picture 1:
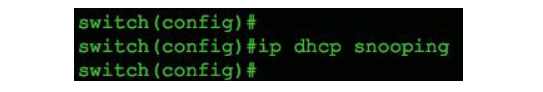
(This setting is for a Cisco Switch)
Step 02: Use the command ip dhcp snooping vlan 99 to protect the VLAN need to be protected. As shown in the following pictures 2 and 3, you can range a sequence of VLANs beside only VLAN 99.

(Only VLAN 99)

(a sequence of VLANs)
Step 03: The final step is to let the switch know the port to which a trusted DHCP server is attached. Look at the following picture 4.
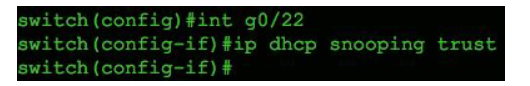
(Trusted port configuration for authentic DHCP servers)
Things You Should Know About DHSCP Snooping:
Traffic Dropped By DHCP Snooping:
DHCP snooping will drop the traffic /messages that are coming from untrusted DHCP servers. DHCP trusted servers are recognized by configuring DHCP snooping on a switch. It prevents the flow of traffic coming from an untrusted source.
After a network administrator applies DHCP snooping in an operating system, DHCP snooping maintains a database that stores devices’ MAC addresses, DHCP-assigned IP addresses, remaining lease time, VLAN, and switch port. Through this database, DHCP tracks the information and distinguishes unauthorized messages from authorized ones.
Where Can I Deploy DHCP Snooping?
Where should I deploy DHCP snooping? The question dates back to the starting days of this then-new emerged feature. If you are stuck on it, we have come to provide you with a genuine answer.
Local Area Networks: In homes or offices where multiple devices are connected to the network. DHCP provides a unique address IP address automatically to every device which simplifies network management.
WiFi Networks: DHCP snooping can be deployed at cafes, libraries, and shopping malls. DHCP provides temporary IP addresses to visitors to help them access the resources easily.
Enterprise Networks: In large-scale businesses, organizations, and firms where hundreds of devices are connected at the same time, DHCP jumps in and helps network administrators simplify IP management. Additionally, it increases network security and overall network performance.
Internet Service Providers: When you set up a router in your office, ISPs use DHCP to assign an IP address to your device. It makes the process smooth and prevents user intervention.
VPN and Cloud Environment: In Scenarios like virtual networks and cloud-based services where temporary or dynamic resource allocation becomes necessary, DHCP snooping plays its role manage make virtual machines work efficiently.
Conclusion:
DHCP snooping has been rocking the networking industry ever since it entered in the market. Especially in environments where security is paramount and devices in plenty are needed to connect at the same time. Provides features like security, enhanced performance, simplified management, and ease of installation, it eliminates the headache of reclaiming IP addresses manually on a daily basis. Thus, wrapping up the story, we hope to have provided you with a comprehensive guide on DHCP snooping, its concepts, and configuration. Remember, we don’t stop here; just hit us up whenever you need to know something new about the ever-changing world of networking. Thanks.
Frequently Asked Questions:
What are the two main benefits of DHCP snooping?
DHCP or Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol snooping provides many features. However, at its core, two main benefits a network administrator enjoys are: First, it guarantees that DHCP clients get IP addresses only from trusted and authorized DHCP servers. Second, DHCP snooping, when enabled in a Cisco switch or any other device, makes a device maintain a record of IP addresses and MAC addresses of DHCP clients resulting in no DHCP attacks.
What is a static IP?
Static IP addresses refer to the type of address that does not change over time. Unlike a dynamic IP address that keeps itself changing for some intelligible reasons.
What is DHCP and why do we use it?
A DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) is a protocol to provide an IP address automatically. It is used to automate the process of configuring devices on IP networks. It is used to eliminate the problem of reclaiming IP addresses manually. Plus, it provides security features that protect network operations from hackers and unauthorized individuals.
What is the difference between DHCP and DHCP snooping?
DHCP servers assign IP addresses to clients on a LAN. On the other hand, you can configure DHCP snooping on LAN switches to disallow untrusted DHCP servers and prevent malicious or unwanted DHCP traffic.
What are the common use cases of DHCP snooping?
DHCP snooping can be deployed in Local Area Networks, WiFi Networks, Enterprise Networks, Internet Service Providers, and VPN and Cloud Environments. All these scenarios can be equipped with modern DHCP features by enabling DHCP snooping.




 Catalog
Catalog