Understanding WLAN: A Complete Guide to Wireless Local Area Networks
Table of content
Introduction:
In the present networking landscape, Wireless internet is preferred over wired connections. What has been taking their place is known as WLAN or wireless Local Area Network. This connection enables you to connect your devices to the internet without any need for a wired connection. In addition, it facilitates consumers and businesses in achieving their internet-related tasks from anywhere at the same time. If you are curious to learn more about a WLAN and its different aspects, this blog post is meant for you. We will discuss Wireless LAN in detail throughout this blog.
What is WLAN?
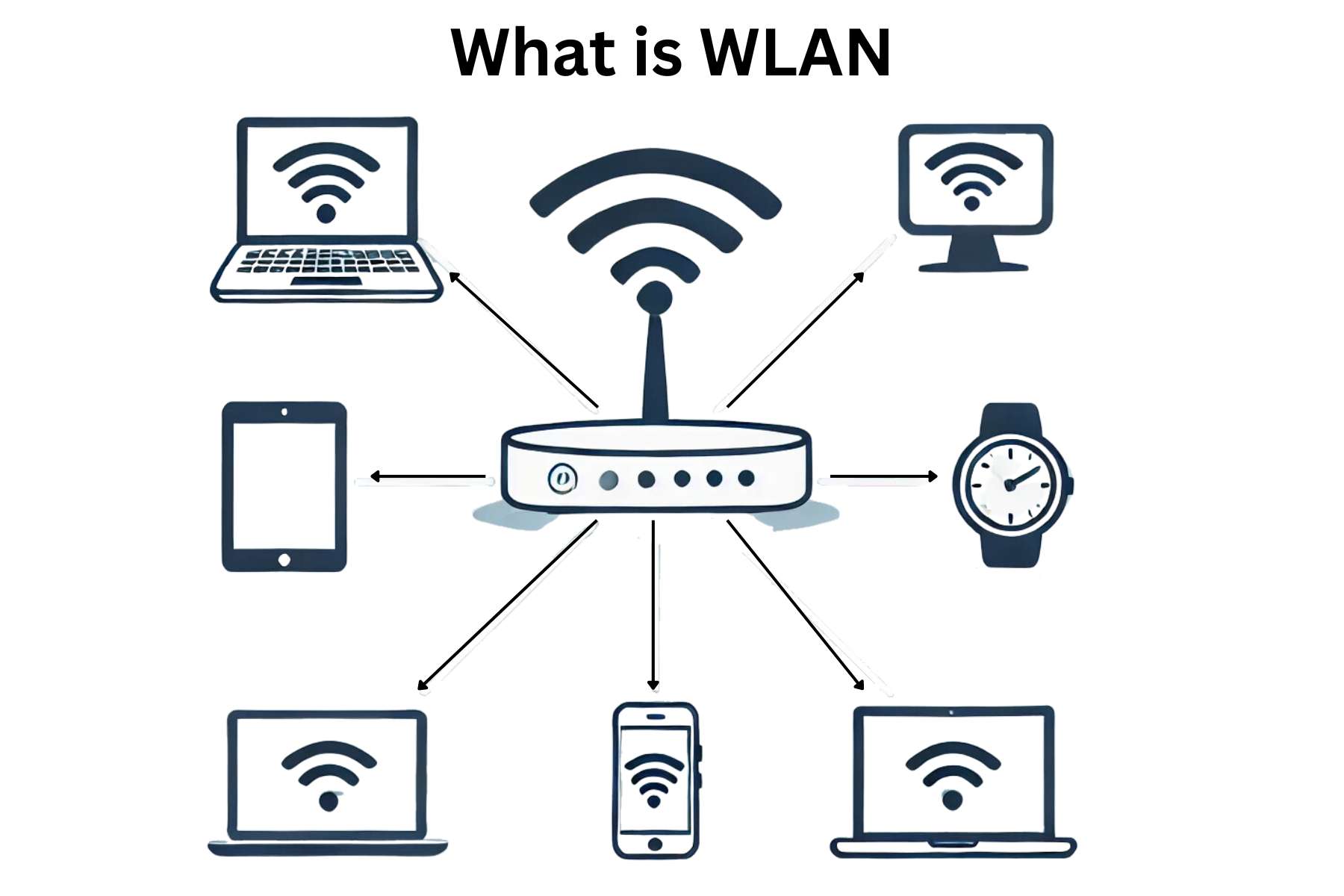
A WLAN network or wireless LAN is a wireless network that connects various devices wirelessly on a LAN. Unlike wired networks, it uses high-frequency radio waves and sometimes an internet access point.
By enabling connections between devices without the need for physical wires, wireless LANs have greatly increased convenience and allowed for increased mobility and ease of use in a variety of settings. The best example and brand of a WLAN is WiFi, which uses IEEE 802.11 specifications.
A wireless Local Area Network has brought a lot of comfort revolutionizing the entire internet technology. Not only it facilitate people to connect devices wirelessly, it also enables them to access the internet without being stationed at a particular point in their workplace or home.
WLAN Architecture:
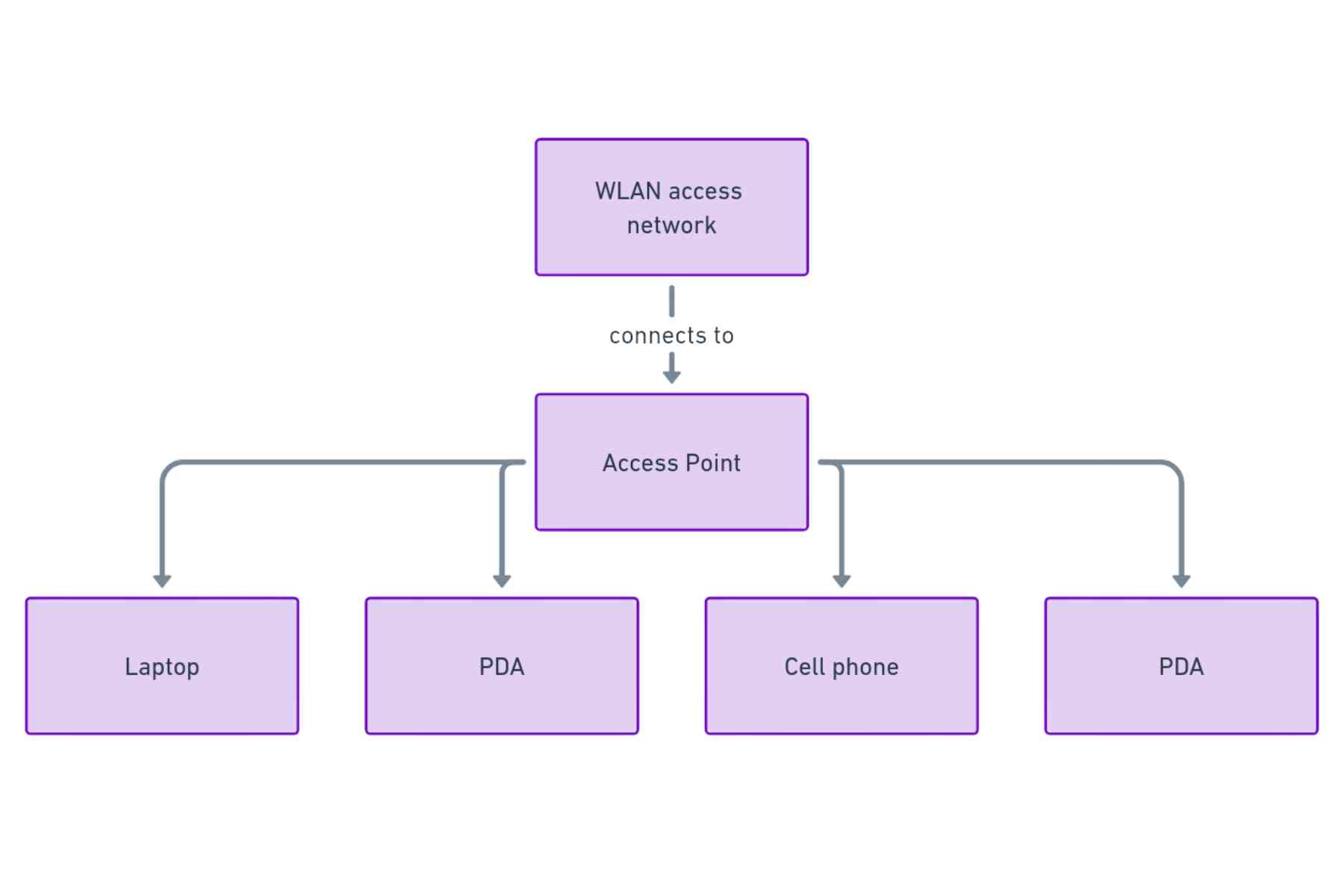
Stations:
All components connected wirelessly to networks are called stations. They are either points or endpoints with their unique network addresses.
Basic Service Set (BSS)
That device is a network connection station. The collection of stations is called an Independent BSS (IBSS) in ad hoc networks. An Extended Service Set (ESS) is a collection of linked BSSs, such as those found in a network with several access points.
Distribution system:
These systems connect access points in an ESS. The connections are either wired or wireless. A wireless distribution system (WDS) uses mesh or its own WDS protocol.
Access point:
The base station that acts as a hub for other stations to connect to is known as the access point. While many routers also function as internet modems, the term “access” may also refer to a station’s ability to access the internet. Access points in an ESS can be wired or wirelessly connected via Ethernet cables.
Bridge:
The bridge connects a WLAN to a LAN or an access point.
Endpoint:
The endpoint is any end-user station, such as a computer, mobile device, printer, or Internet of Things (IoT) device.
Devices on a WLAN (Wireless Local Area Network)
Now that you have understood the wireless LAN meaning, the next question is, what type of devices can you connect on a WLAN? So it can connect a number of devices from two or three to hundreds. However, it is important to keep in mind that the growing number of devices can make your wireless Local Area Network complicated and challenging.
Some common devices that a wireless LAN can accommodate include portable computing devices, such as laptops, tablets, and mobile phones. Additionally, they can connect video game consoles, IoT devices, and internet audio platforms.
What Is The Difference Between LAN and Wireless LAN?
A LAN connects devices in proximity and includes both wireless and wired connections. Then, how does a wireless LAN differ from a LAN? Here is your answer:
| WLAN (Wireless Local Area Network) | LAN (Local Area Network) |
| It stands for Wireless Local Area Network. | LAN stands for Local Area Network. |
| These connections are completely wireless. | LAN connections include both wired and wireless connections. |
| It is a group of computers or other such network devices in a particular location that are connected together wirelessly. | It is a group of computers or other such network devices in a particular location that are connected together either wirelessly or through a wired connection. |
| It is sensitive to external attacks. | LAN is safe from cyber-criminal attacks. |
| It is not safe and secure. | Comparatively it is safer. |
| It is popular. | LAN network is no longer much famous due to the latest wireless networks. |
| Works on connecting wires to the switches and routers are neglected. | Wired LAN needs physical access like connecting the wires to the switches or routers. |
| Ethernet cable is not necessary. | Devices are connected locally with Ethernet cable. |
| Excellent mobility. | Mobility is limited. |
| It changes because of external factors like environment and quality of cables. | It may or may not vary with external factors like environment and quality of cables. |
| It is more expensive. | LAN is cost effective. |
| Limited by signal strength (up to 100m) | Limited by cable length (up to 100m per segment) |
| Requires strong encryption (WPA3, WPA2 | Generally, more secure, physical access needed |
Types of WLAN (Wireless Local Area Network)
Anyone can ask you what type of WLAN you are going to design for your networking environment. To answer this question and set a suitable wireless LAN, you must know different types of wireless LAN. So, here are some of the common types that are mostly considered today:
Infrastructure:
This is the most common type of wireless LAN and relies on wireless devices to connect to the WAP (Wireless Access Point). This means that the devices you want to connect to the network should be within the WLAN range and authorized to join it.
Ad hoc:
In contrast to infrastructure mode, an ad hoc network doesn’t rely on a wireless access point or WAP. Instead, stations communicate peer-to-peer in these networks. This peer-to-peer network enables wireless devices to connect with each other. Then, there can be a smooth and safe data transmission.
Bridge:
A bridge is used to connect one network to another. A wireless ethernet bridge enables devices to connect to a wireless network that are already connected to a wired ethernet.
Wireless distribution system:
A WDS (Wireless Distribution System) enables wireless interconnection of access points in an IEEE 802.11 network. It uses multiple access points and expands the network without relying on wired infrastructure.
Advantages and Disadvantages of WLAN:
Advantages of Wireless Local Area Network:
- Reliable for most scenarios and users.
- A versatile way of communication as it reduces wired connection.
- Also lowers the ownership value.
- Easy to manage.
- Provides high-speed connectivity in a small coverage area.
- You don’t need a bunch of cables to install it.
Disadvantages of Wireless Local Area Network:
- In some cases, it requires a license, which can be a hurdle for consumers and businesses.
- Limited to a small and limited area.
- Data transfer rate decreases with the growing number of connected devices.
- Uses a frequency that can interfere with the frequency of other devices.
- Can easily be attacked because of lower security.
- More expensive than wires and hubs.
- Can go down in situations like rain or thunder.
How To Set Up a Wireless LAN:
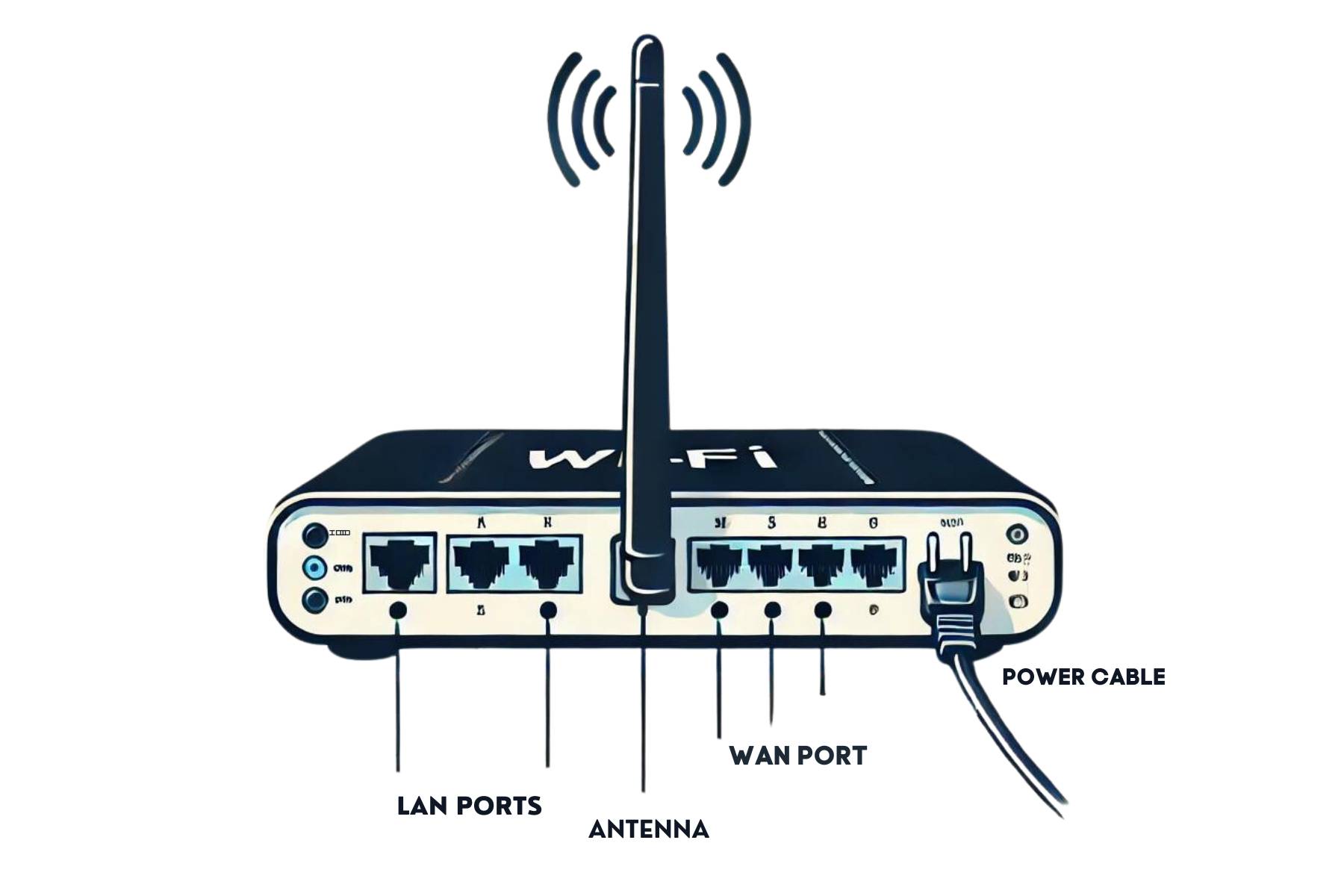
There are some simple and technical steps that you follow to set up a successful wireless LAN in your system. These steps include some equipment, such as a wireless router, an internet connection through an Ethernet cable, and powerhouse.
First of all, connect your wireless router to the internet source to the power outlet. You can set a name of your own choice as it helps lessen the privacy risks. Otherwise, the network has a default name.
There are some documentation processes that come along with a wireless router and you need to go through them to enable WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy) security. You can set recommended security features as mentioned in the documents of your router.
In other cases, you can use an access point if you don’t want to use a wireless router. An access point is placed in a central location.
These steps lead you toward a successful installation of a wireless local area network.
Conclusion:
Whether it is a WLAN or any other wireless connection, people are moving towards a new internet age. From households to businesses, wireless internet connections have become the first priority of almost every network architecture. Therefore, we have provided you with this insightful blog to inform you about WLAN, from its types to features and the pros and cons of the installation process. Still, if you ever feel stuck anywhere, you can hit us up without any hesitation. For further insights, visit Buyrouterswitch.
Frequently Asked Questions:
What is a WLAN optimizer?
As the name implies, a WLAN optimizer improves the performance of wireless LAN. It does so by disabling background scans that a network conducts. As a result, it improves latency and lowers lagging.
What is WLAN meaning?
A wireless local area network or WLAN is a collection of devices that are connected together via radio transmission instead of wired connections. The most common example of a wireless LAN is WiFi.
Are Wi-Fi and WLAN the same thing?
WiFi is a type and example of wireless networks but not all Wireless Local Area Networks are WiFi. All other types of radio transmissions that connect Local Area Networks or LAN nodes are also wireless LANs. But, the most common type of Wireless LAN is WiFi which is mostly used today.




 Catalog
Catalog




















































































































 (800) 870-9487
(800) 870-9487