POTN Secrets: What the Experts Won’t Tell You
Table of content
Introduction:
POTN (Packet Optical Transport Network) integrates flexibility and scalability of packet switching and high-performance and bandwidth of optical transport, providing users with efficient communication networks. It has changed the way optical networks function and grow. In addition, by combining the capabilities of PTN (Packet Transport Network) and OTN (Optical Transport Network), POTN caters to the unique needs and requirements of various networking applications. If you have queries related to packet OTN and want to explore the wonders of Packet Optical Transport, read this blog carefully; in this blog, we will discuss the Packet optical transport network’s definition, components, features, applications, and reasons that compel users to choose it.
What is POTN:
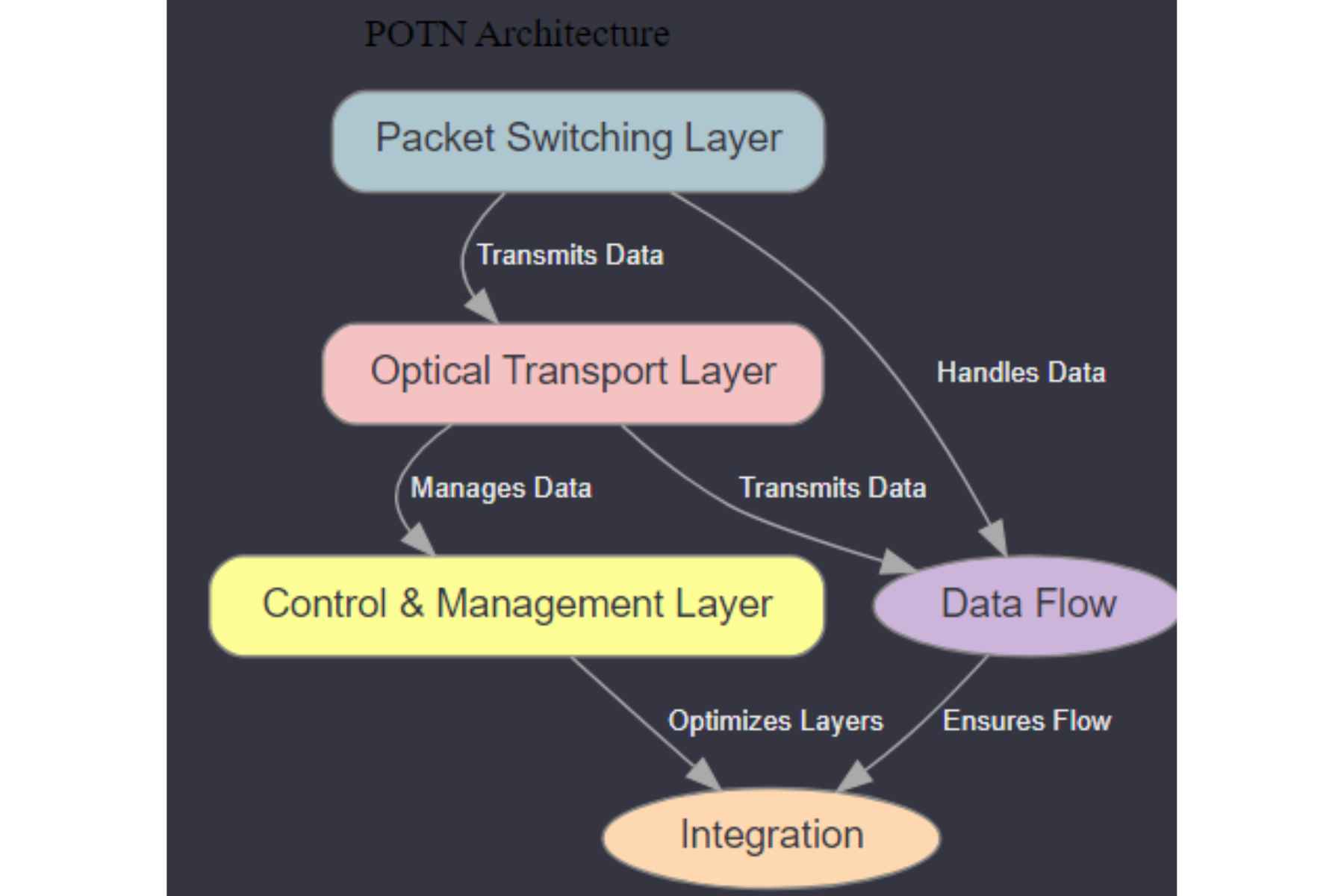
A Packet Optical Transport Network (POTN) combines the benefits of optical and packet-switching technologies. It uses optical fibers to carry data over long distances quickly and efficiently. At the same time, it incorporates packet-switching to manage and route data more flexibly. This hybrid approach allows for high-speed data transmission and better handling of varied traffic types, making networks more reliable and scalable. P-OTN is especially useful for supporting the growing demand for high-bandwidth applications like video streaming and cloud computing.
Why To Choose POTN (Packet Optical Transport Network)?
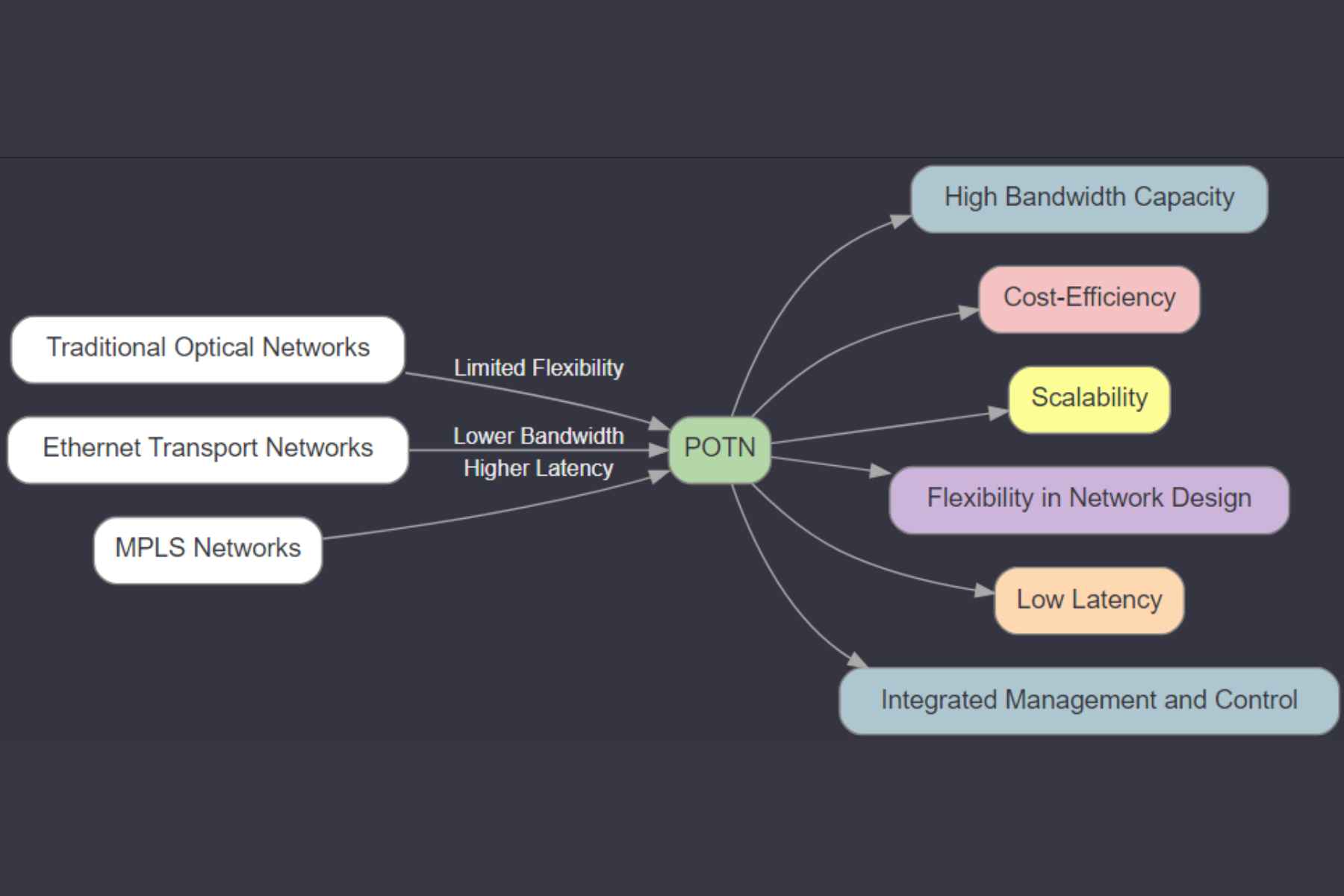
Packet optical transport network provides multiple features and benefits for different organizations. Some of its main benefits and reasons that compel businesses to choose it are mentioned below:
Convergence of Packet Switching and Optical Transport
It offers a unified network architecture by integrating all the benefits of optical transport and packet switching. It enables the effective transfer of packet-based data and conventional circuit-switched traffic over the same network.
Flexibility In Services
It provides flexibility in terms of services offered. It is appropriate for a variety of applications and client demands since it allows for a broad range of services, such as voice, data, and video.
Bandwidth Efficiency and Switching Capabilities
Packet Optical Transport System can effectively use network bandwidth by dynamically distributing resources based on demand through its packet-switching features. This guarantees effective resource use and helps maximize network utilization.
Scalability For Growing Networks
Because of its great scalability, network operators may quickly increase the capacity of their networks in response to growing traffic needs. It offers the flexibility to support future development and the addition of additional services without causing major disruptions.
Cost-Effectiveness
Through optical transport and packet switching technology, it can provide network operators with affordable solutions. It makes network management easier, lowers operating costs, and allows the aggregation of several services onto a single network infrastructure.
Fiber Optic Devices Used In POTN:
In scenarios where light signals are transmitted and received over longer distances, networks use fiber optic devices. These devices are purpose-made, reliable, and efficient. A fiber optic device is capable of transmitting data at higher rates. Some common devices that are used in packet optical transport networks are mentioned here:
Optical Line Terminals (OLTs):
Found at a network provider’s central office, OLTs connect to several ONUs at client locations. Besides, traffic between ONUs and the main network is consolidated and routed by OLTs.
Optical Network Units (ONUs):
ONUs connect to the OLT at the central office from customer premises. Customers can get a range of services from ONUs, including voice over IP (VoIP), television, and broadband internet.
Optical Add/Drop Multiplexers (OADMs):
Using optical add/drop multiplexers (OADMs), optical signals from a fiber optic connection can be added or dropped. They are employed in the construction of ring networks and in the interconnection of various network components.
Switches for fiber optic networks:
Optical communications are routed between ports using fiber optic network switches. They can link several segments of a ring network together, link OLTs and ONUs in a PON, or link Packet Optical Transport Networks to other networks. Features including multiple ports, backup power sources, and compatibility for high-speed data rates are available in fiber optic network switches.
Modules for SFP:
Optical transceivers are connected to fiber optic network switches and other devices using SFP modules. They provide an adaptable and affordable means of joining optical transceivers, providing a broad spectrum of transmission lengths and data speeds.
Trends That Make Packet Optical Transport Network Important:
Why POTN is important? And why do we see a rapid increase in its demands worldwide? Answers to these questions are hidden in the factors that have emerged in recent years. Some of the main trends and factors that drive the adoption and requirements of packet optical networks are discussed here:
Emergence of 5G:
To support a huge increase in data volumes and traffic, 5G networks demand high-performance, scalable, and flexible transport architecture. By providing flexibility, scalability, and bandwidth efficiency, POTN provides the ultimate solution for 5G transport.
Rise of Cloud Computing:
Cloud computing is another factor that makes the Packet Optical Transport System important. Cloud providers require a reliable and high-performance infrastructure to supply their services to clients by connecting their data centers. POTN provides them with an ideal solution for cloud transport. It offers the flexibility, scalability, and bandwidth required in the rapidly growing market.
Demand for Increased Bandwidth:
As data-intensive applications and services grow rapidly, the requirement for enhanced bandwidth also increases. Packet optical transport offers the best solution to these services. It supports the ever-growing traffic volumes by providing these platforms with flexibility, scalability, and higher bandwidth according to their needs.
POTN (Packet Optical Transport Network) Applications:
According to the application scenarios and uses, POTN can be divided into four major categories. These categories are made according to the network level and requirements of businesses. Here is an explanation of Packet OTN applications:
True Linke:
In such environments, POTN completes the flexible scheduling and aggregation function of small to mid-sized services based on L2/L3 and the large-bandwidth, large-granularity, and long-distance transmission functions. Besides, it fulfills the need for traditional trunk OTN and group business interfaces.
Metro Transport Network:
POTN handles the flexible scheduling and aggregation of different small and mid-sized businesses. In addition, it increases network-side bandwidth with the help of technologies like PIC.
Home Broadband:
Packet OTN is largely applied for covering the OLT’s upstream home broadband services and carry out large-bandwidth and low-cost transmission and scheduling of these services.
Group customers:
These services are transmitted through flexible pipes, allowing for adaptable forwarding and access. For high-value inbound services, CBR boards can be used to connect to the POTN network. These services are transmitted through rigid pipes, providing large bandwidth, low latency, and high security.
Conclusion:
POTN is a perfect fit for networks that require flexibility, cost-effectiveness, and high bandwidth. It combines all these features by integrating the capabilities of optical transport technologies and packet transport. These networks can be applied to various scenarios, including group customers and home broadband. In this blog, we have provided you with the best possible guide on Packet Optical Transport Networks. In the end, we invite you to buyrouterswitch.com to read further topics like LAN vs WAN, Optical Network Terminal, Fiber Optic Cable, and Fiber Optic Modem.
Frequently Asked Questions:
What is a packet-optical network?
Packet optical network provides universal aggregation and transport infrastructure that are the base for all present and future Ethernet and IP services. It has completely changed the scene for next-generation IP networking.
What is the difference between OTN and Ethernet?
The multiplexing method used by Ethernet and OTN differs significantly. Ethernet allows the framing of data with a variable bitrate into frames with a variable length. In contrast, OTN is based on framing data into fixed-length frames on fixed data-rate channels.
What is POTN in telecommunication?
Packet-optical transport Network (POTN) technologies and infrastructure combine the functional switching capability of WDM wavelengths, Ethernet through different protocols, OTN/ODU as well as TDM.




 Catalog
Catalog





















































































































 (800) 870-9487
(800) 870-9487