MB vs GB: Understanding Data Storage and Transfer Units
Table of content
Introduction:
Imagine downloading, sharing, or just going through pictures, videos, and songs on your mobile phone. GB, MB, and Bit are the concepts you encounter at every step. Especially, gigabytes (GB) and megabytes (MB) are the most used units of data storage or memory in our daily lives. We always keep our eyes on how many megabytes a video is when we download it or how many gigabytes an application, software, or game is when we are going to purchase them for business or personal use. It is a fact these measurements have become a permanent part of our memories, but still, there are some complexities that need to be addressed, and hence, we are here with an informative and research-driven article. So, go ahead and dive deep into ‘MB vs GB.’ There is almost everything you need to or ought to know.
MB vs GB: What is the Difference?
A megabyte (MB) is a data measurement unit that uses thousands of bytes in order to transmit and store digital information. Simply, a megabyte equals one million bytes. From an advanced point of view, it is composed of 1,048,576 bytes of computer memory and one million bytes of computer storage. Below are some illustrations to give a crystal-clear idea about MB (megabyte):
- A compressed version of a 6=4-megapixel JPEG is approximately 1 MB in size.
- DNA encodes the human genome, which is composed of 800 megabytes.
- One minute of MP3 compressed music at 128 kbit/s.
- A bitmap picture of 1024*1024 pixels and 256
- In plain text format, a standard English book volume.
- Six seconds of uncompressed CD audio.
- A quality book volume of the English language.
- Six seconds of uncompressed Audio CD.
A gigabyte (GB), referred to as a media storage data measurement unit or a digital device, is a combination of a number of bytes to store digital information. Simply, A gigabyte is equal to approximately 1024 MBs or megabytes. In terms of disk storage and data transmission number in communication, a gigabyte is one made up of one billion bytes. These days, individuals from the field of networking have some confusing interpretations of GB, such as ‘gigs.’ These gigs calculate the capacity of storage devices. For instance, you can store 4.7 GB of data in a standard DVD drive. To be more advanced, Terabytes are storage devices with a capacity of one thousand GB of data. Some common examples of GB are mentioned below:
- Uncompressed CD-quality audio of 114 minutes is equal to about 1 GB.
- A dual-layered Blu-ray disc can have the capacity to hold 50 GB of data.
- The size of an HDTV video of 7 minutes equals 1 GB.
- 7 GB of data can be held by a DVD-R.
GB vs MB vs KB – In a Nutshell
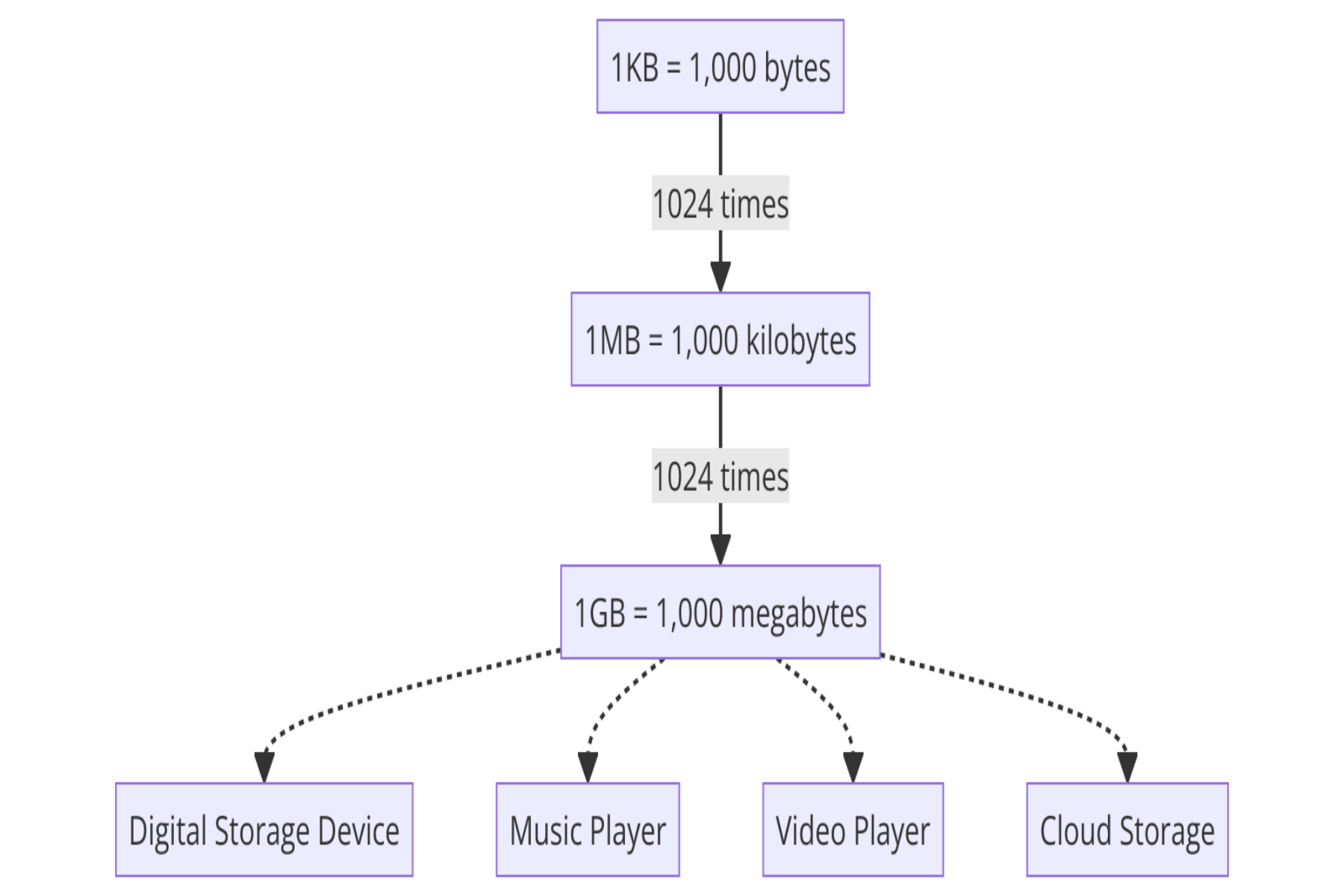
These terms have already been discussed, and you are familiar with them. So, it is nothing but a waste of time to read about them again and again. Instead, it can be of huge significance to put GB vs MB vs KB face to face to reach a conclusion. Let’s look at them in a hierarchal manner:
- GB (GigaByte) > MB (MegaByte) > KB (KiloByte)
- A GigaByte is made up of approximately 1024 MegaBytes.
- A MegaByte is composed of about 1024 KiloBytes.
- A Kilobyte is made up of approximately 1024 Bytes.
Conclusion:
GB, MB, and KB are the specific units of data measurement. A KiloByte is smaller than a megabyte, and a megabyte is smaller than a gigabyte, respectively. We have discussed some broader concepts and terminologies related to these units. Plus, we addressed some important and basic queries that arise when one thinks of ‘MB vs GB.’ Still, if you have queries, don’t hesitate to hit us up.
Frequently Asked Questions:
Which one is bigger, MB or GB?
A simple answer is GB is bigger than MB. There are approximately 1024 MB in one GB. In comparison to gigabytes, megabytes are smaller and equal to one million bytes.
How many MBs are in 1 GB?
There are approximately 1,000 in 1 GB. The amount of GBs on your SIM plan decides the amount of data you can use in one month.
Is a GB or MB faster?
“Megabits per second” is represented by Mbps and “gigabits per second” by Gbps. These are data transfer rates, which indicate the rate at which information travels from your router to your device or devices. Megabits and gigabits are very different in size; a gigabit is equivalent to 1,000 megabits.
Learn more: GB vs MB




 Catalog
Catalog




















































































































 (800) 870-9487
(800) 870-9487