Coaxial Cable Guide: Types, Benefits & Working
Table of content
Introduction:
Why are coaxial cables still relevant when they are less efficient than optical fiber? Being introduced in the early 20th century, these cables are still used by mobile and internet companies to transmit data, video, and voice communications to users and customers worldwide. But, what is a coaxial cable? What does it look like? Why do we use it? These questions are the most asked questions today. Therefore, we are going to answer these questions, along with some others, in a simple way. So, read this blog till the end and learn everything about a coax cable.
What Is a Coaxial Cable?
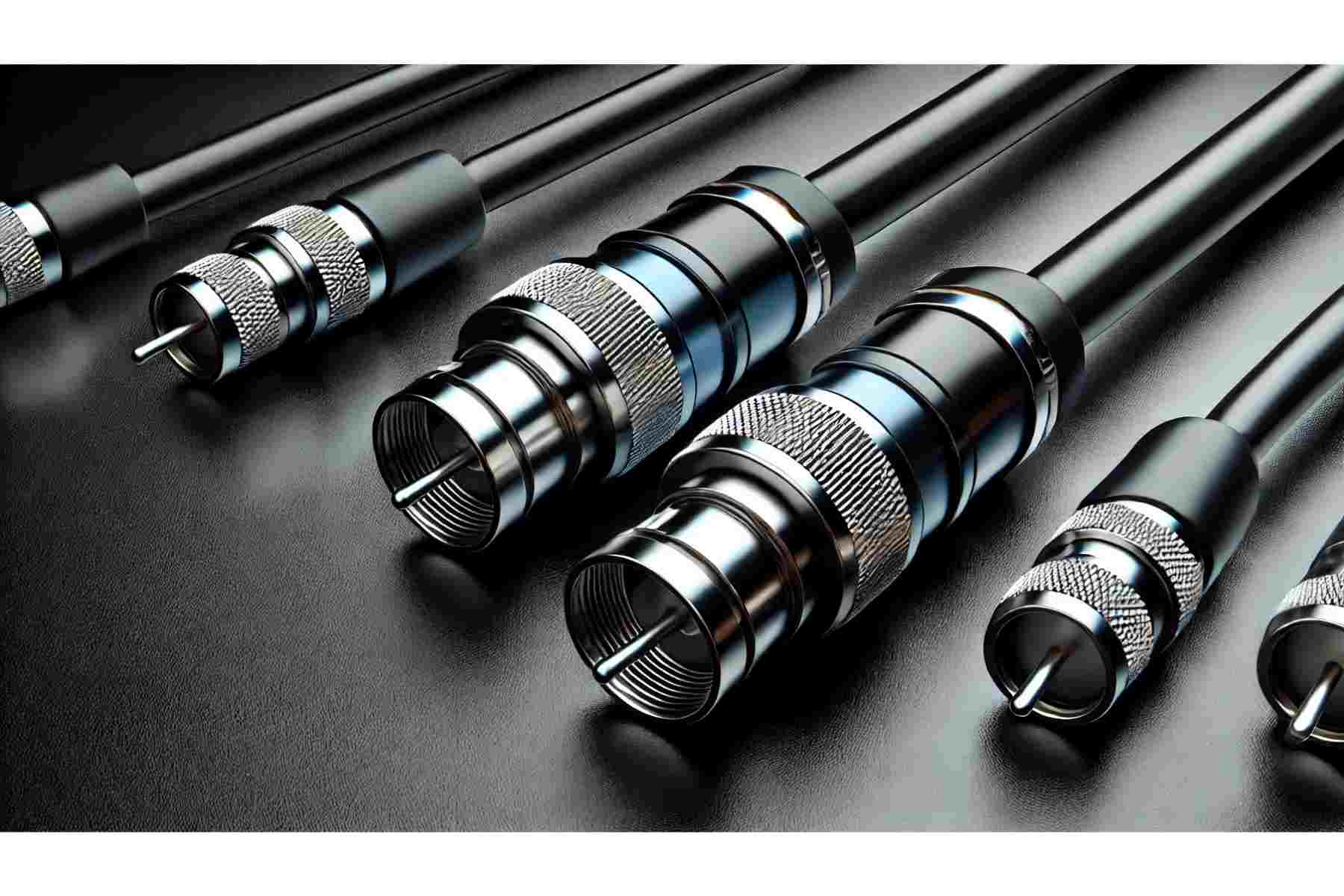

A coaxial cable is an electrical cable that easily transmits Radio Frequency (RF) signals from one point to another without losing them. It is cylindrical in shape and has an outer and an inner core, as shown in the picture above. This design prevents EMI (Electromagnetic Interference) and makes data transmission smoother and more reliable.
Historically, coaxial cables have been used to transmit signals in electrical form rather than light form. This is the reason that they are less efficient than optical fibers but have more bandwidth as compared to optical fibers. Coaxial cables are used in various fields, such as satellite television signals, telephone lines, and cell phone signal boosters. Today, they are available in a variety – where each type offers a specific function.
What Does a Coaxial Cable Look Like?

As compared to other types of cables like Ethernet cable, twisted pair, and Ethernet crossover cable, coaxial cables have a distinct and thick design. They are round in shape because of the inner insulation layer. As per the structure of a coaxial cable, there are four main parts of the structure which include:
Copper Conductor: It is a central conductor that contains copper.
Insulator: It is dielectric plastic insulation around the copper conductor.
Braided Mesh: It prevents electromagnetic interference.
Protective Plastic Layer: It protects internal layers from damage.
How Does a Coaxial Cable Work?
As we know by the structure of a coaxial cable, it has a center copper wire and a metal shield. Both these conductors receive a current at the same time and create a magnetic field. Along with this magnetic field, the shield keeps the signal in the field and prevents it from going out of the flow resulting in zero signal loss. In addition, the copper wire restricts all sorts of electromagnetic interference. As a result, coaxial cables can carry signals over long distances without experiencing any disturbance.
Coaxial Cable Types:
Coaxial cables are available in a variety. Each type of cable is recognized on the basis of their specifications, applications, and resistance they may have. In this section, we will briefly explore all types of coax cables.
RG-6/U
This is the most common type with a resistance of 75 Ohm. It is used in households, businesses, and many other applications widely.
RG-8
Similar to RG-6 but cannot carry original video signals, It has 50 Ohm resistance and is mostly used in audio control rooms and radio stations. Besides, it can be used as a connection for external radio antennas.
RG-11
It is a higher gauge cable that is applicable in scenarios with CATV, HDTV, TV antennas, and video distribution. It provides 3 GHz frequency with a resistance of 75 Ohm.
RG59
These are some of the most common types of coax cables comparatively lower in performance. Their architecture is flexible with rigid shielding and thick insulation. Despite being not well protected they still do not allow any interference.
LMR – The New Generation of Coaxial Cables:

This is the new generation and future of coax cables. These cables are more flexible with ease of installation and competitive rates. They are mostly used for antennas on missiles, airplanes, ships, satellites, and communications as transmission lines.
LMR 200:
Flexible low-loss communications cable with an outdoor rating. With a 50-ohm impedance, it’s ideal for short antenna feeder runs. Low PIM is another feature of this.
LMR 240:
Another flexible low-loss communications cable with an impedance of 50 Ohm that is rated for outdoor use is LMR 240. It is intended for brief feeder lines for mobile antennas, WLAN, and GPS, among other uses.
LMR 200:
It is another flexible low-loss communications cable with an outdoor rating. With a 50-ohm impedance, it’s ideal for short antenna feeder runs. Low PIM is another feature of this.
LMR 240:
LMR 240 is another flexible low-loss communications cable with an impedance of 50 Ohm that is rated for outdoor use is LMR 240. It is intended for brief feeder lines for mobile antennas, WLAN, and GPS, among other uses.
LMR 400:
The flexible communications coax LMR 400 has a 50 Ohm impedance. It is utilized for short antenna feeder runs and jumper assemblies in wireless communications systems. Select this cable if you need one that needs to be bent repeatedly or on a regular basis. The RG-8 cables were intended to be replaced with LMR 400.
LMR 600:
The LMR 600 “Half Inch” is also intended for outdoor use. It can be bent and handled more easily than hardline and air-dielectric cables. Additionally, it features a 50-ohm impedance.
LMR 900/1200/1700:
The bigger LMR 900, 1200, and 1700 cables are made for medium antenna feeder runs in any application where a flexible, low-loss cable that can be easily routed is needed.
Uses and Applications Of Coaxial Cables:
As mentioned earlier, coaxial cables are largely used today. From telecom companies to internet providers and households, these cables are almost everywhere. In each situation and scenario, a specific type of coax cable is used for particular tasks. For example, if your home has a satellite TV, you must have a coaxial cable that can be used to attach the TV to any other streaming device. Some other use cases and application scenarios are mentioned below:
CCTV:
RG-59 is a prime option for scenarios like security cameras or CCTV. If you have longer distances, you can also use RG-6. However, each cable can have some hurdles. For instance, RG-59 is easier to handle than RG-6 because it is longer, thicker, and firmer.
Video:
For video, RG-6 and RG-59 are the most common options mainly considered. The aforementioned is recommended for digital signals, while RG-59 is an industry standard.
Internet:
Coax cables are also used to transmit internet connection signals. It is important to remember that these signals run at a higher frequency than traditional analog signals. RG-6 is the best coaxial cable for the internet that fulfills these requirements.
You may laugh here, but RG-6 is once again recommended for television use. For the best quality TV reception, use a cable within 75 Ohm; otherwise, your cable will result in poor TV reception.
HDTV:
As the name implies, HDTV means stronger signals. Cables that are used for such scenarios require more space for signal transmission. So, the best choice is an RG-11 for HDTV (High-Definition Television)
Features of a Coaxial Cable:
- These cables are Inexpensive.
- They are easy to wire and install.
- They can be expanded easily.
- They have good resistance to EMI (Electromagnetic Interference).
- They have a capacity up to 10Mbps.
- These cables are durable.
- Compatible with older 10BaseT networks.
- Have higher speed.
How To Choose the Best Coaxial Cable?
RG (Radio Guide) number doesn’t reveal everything about a coaxial cable; there are some other factors that should be considered when choosing a coax cable for your applications. So, here are some steps that can be used as a roadmap:
Application:
The first thing to consider is whether you need a short- or long-range cable and low or high frequencies. For example, you can use another type of cable for military operations, but the requirements change regarding general use.
Resistance:
It may be the most important thing in a coaxial cable. It is expressed in Ohms and should match all components of a coaxial cable system, helping prevent all sorts of hurdles in signal transmission.
Environment:
You should adapt strategies according to the environment. For example, if coaxial cables are installed underground, they should pass through waterproof pipes for protection for liquid and vapor permeation.
Working Voltage and Power Rating:
The voltage of a coaxial cable passes through the center wire. Each cable has a unique voltage (Maximum or Peak). This voltage can be reduced for safety.
Signal Loss at Specific Frequencies:
These cables can experience a signal loss at VMH (Very High Frequencies) and UHF (Ultra-High Frequencies). To prevent VHF and UHF interference, some vendors and manufacturers provide a foil or braided shield.
Conclusion:
Signal transmission with pure quality and high speed is the need of every telecommunication system. That is where we encounter a coaxial cable with all its types of categories. In the present blog, we have gone through different aspects of a coaxial cable to let you know about its features, types, and use cases. In addition, you can use this blog as a guide when choosing a coaxial cable.
If you are interested in reading topics like fiber optic cable, displayport cable, and SATA cable or want to explore network accessories like switches, routers, and firewalls, you can visit Buyrouterswitch.
Frequently Asked Questions:
What is a coaxial cable splitter?
A coaxial cable splitter is used in video transmission branch of a single video feed to multiple places. Coax cable splitter come in 2, 3, 4, and 6 way configurations. They maintain the proper resistance environment on both the input and output ports.
What is coaxial cable connector?
A coaxial cable connector is designed to maintain the shielding on the table and is used to connect cables to other devices. High-quality connectors offer reliable and long-lasting connections. They are two in style: one is called male and the other female.
What is the difference between coaxial cable and regular cable?
Coaxial cables are mainly used for internet connections and cable television. On the other hand, regular cable or twisted pair cables are used for telephone communications. Secondly, a coaxial cable supports greater length. Twisted pair cables are less expensive and thicker.




 Catalog
Catalog




















































































































 (800) 870-9487
(800) 870-9487