Audio/Video Network Guide: Setup, Optimization, and Best Practices
Table of content
Introduction:
At present, the world is striving for unified IP networks where all traffic, whether data or multimedia, is transmitted over the same network. However, linking and handling different types of data on a single network is full of multifaceted challenges when it comes to a particular network design and hardware selection. The reason is every network has its own unique needs, and hence, it is necessary for you to select hardware according to a network infrastructure. It may sound easy for you to tackle all requirements of network design at once, but in actuality, it can trouble you a little more. Therefore, in this blog, we will try to address some of the major challenges linked with designing an A/V Network. Additionally, we will try to provide you with some ways to overcome these challenges/problems.
A/V Traffic Needs:
Live traffic, such as audio and video conferencing, is far different from data traffic. The second one can bear a little delay as long as the data faces no error in transmission. But, in audio and video calls, even a minor jitter or delay can ruin a conversation or webinar in between. Thus, an Audio/Video network must fulfill the following needs:
Latency:
The latency rate should be the lowest in order to ensure that any issues can be sorted out promptly.
Error Rate:
There should be a zero error rate or an error equal to nothing. Particularly for pixel-perfect applications like video editing, that is impossible if pixel transmission is stopped somewhere, as it has to be from the source to the screen.
Throughput:
The network must exceed the throughput performance required to route non-stop incoming audio/video traffic. It can be up to 10GBps or more for some applications.
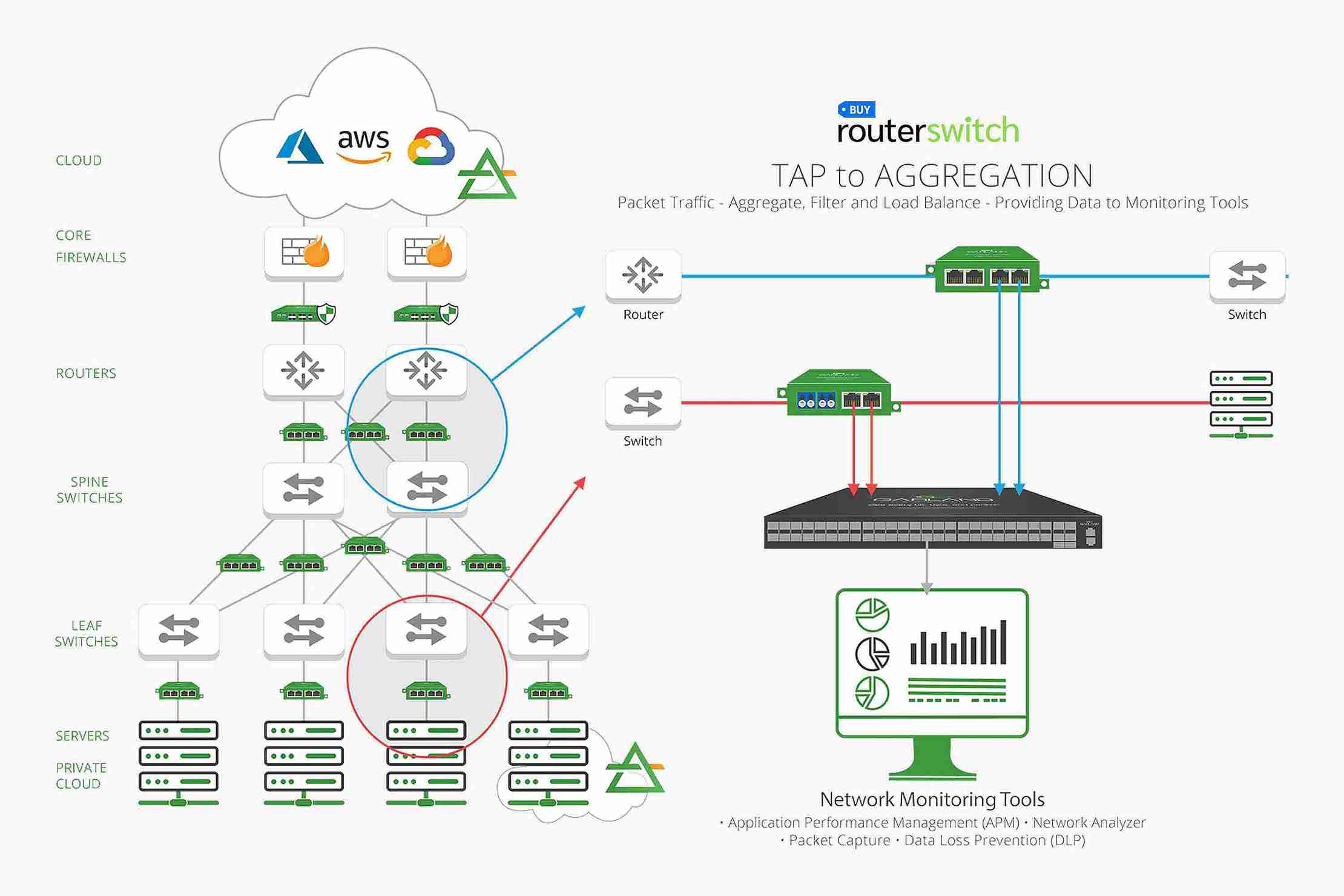
Spine-Leaf Topology:
A spine-leaf design is a data center network topology that comprises two layers switching layers called spine and leaf. The spine-and-leaf topology is one of the most demanding network infrastructures that handles the toughest needs of high-quality AV. It is economical and leaves no room for failure at single points. The leaf layer comprises access switches that combine traffic from the server and link directly to the network core. Spine switches connect all leaf switches in a full mesh topology.
Challenges in Designing an AV Network:
Despite the fact that the spine-leaf topology is a perfect fit for high-quality AV, there are still some challenges to be conquered:
High-Bandwidth requirements:
AV traffic requires a large amount of bandwidth, and hence, a network that offers AV must have a high-speed connection that can tackle a large amount of traffic. It is necessary for video applications where a large amount of data is transmitted in real time.
High-density wiring:
In environments such as stadiums, video conference centers, and theaters where the network has to support a large number of video sources, AV networks need wiring and cabling, particularly.
Quality of Service Management:
In all other types of traffic, AV traffic must be given a high position as it requires priority over other traffic types. Quality of Service management confirms that AV traffic has the priority that is required for its proper and effective functioning.
Network Congestion:
AV traffic can be very weak to network blocking. Therefore, it is very important to have a network that is particularly manufactured and configured to lessen any blocking.
Security:
AV networks can demand extra security features and settings to safeguard crucial data and information that is transmitted over the network. Network administrations must follow stringent security measures to ensure that data is safe and secure.
Conclusion:
To cut a long story short, It can be a daunting task that needs thoughtful consideration of different factors. However, after reading the above-discussed challenges, you must have a roadmap for handling AV network-related problems. In case you need more information or help related to the topic, don’t be shy to contact Buyrouterswitch. We are always ready to guide you to the right track.




 Catalog
Catalog




















































































































 (800) 870-9487
(800) 870-9487